LI Xiao-Ming and CHEN Jiadong 's group published in Advanced Science on the neural mechanism of amygdala in regulating temporal lobe epilepsy
The research team led by Prof. Xiao-Ming Li and Jiadong Chen has recently published an article titled Posterior Basolateral Amygdala is a Critical Amygdaloid Area for Temporal Lobe Epilepsy in Advanced Science on October 30, 2024. This research revealed the pBLA as a pivotal nucleus in the amygdaloid complex for regulating epileptic seizures in TLE.
The amygdaloid complex consists of multiple nuclei and is a key node in controlling temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) in both human and animal model studies. However, the specific nucleus in the amygdaloid complex and the neural circuitry governing seizures remain unknown. Here, it is discovered that activation of glutamatergic neurons in the posterior basolateral amygdala (pBLA) induces severe seizures and even mortality. The pBLA glutamatergic neurons project collateral connections to multiple brain regions, including the insular cortex (IC), bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST), and central amygdala (CeA). Stimulation of pBLA-targeted IC neurons triggers seizures, whereas ablation of IC neurons suppresses seizures induced by activating pBLA glutamatergic neurons. GABAergic neurons in the BNST and CeA establish feedback inhibition on pBLA glutamatergic neurons. Deleting GABAergic neurons in the BNST or CeA leads to sporadic seizures, highlighting their role in balancing pBLA activity. Furthermore, pBLA neurons receive glutamatergic inputs from the ventral hippocampal CA1 (vCA1). Ablation of pBLA glutamatergic neurons mitigates both acute and chronic seizures in the intrahippocampal kainic acid-induced mouse model of TLE. Together, these findings identify the pBLA as a pivotal nucleus in the amygdaloid complex and offer novel circuit mechanisms of pBLA in regulating epileptic seizures in TLE. This insight holds promise for advancing more precise, circuit-targeted therapies for TLE.
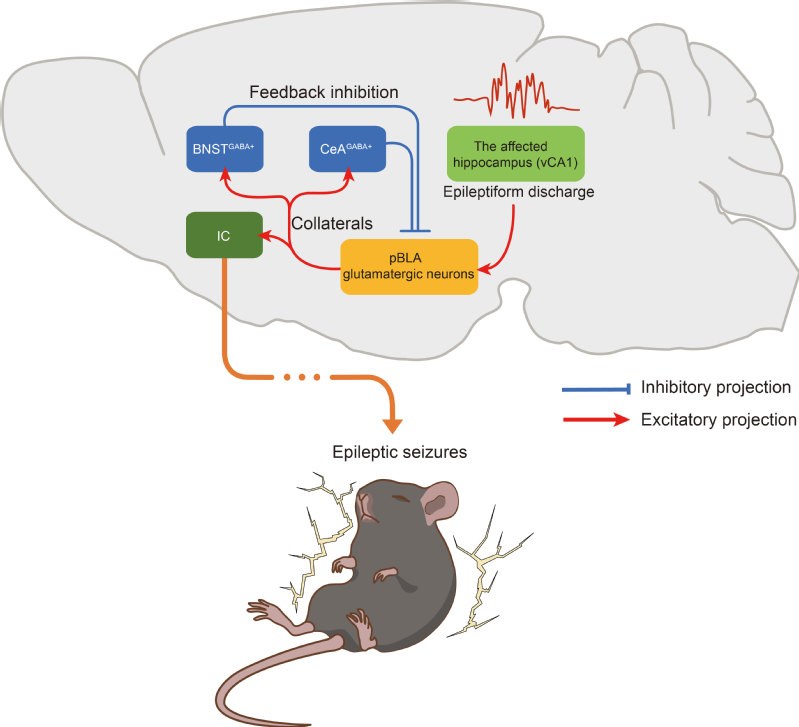
Model diagram showing the role of pBLA glutamatergic neurons and their collateral projections in epileptic seizures in TLE
Website: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202407525
Xiao-Ming Li's RESEARCH GROUP: Dr Xiao-Ming Li's group is focusing on the research of different synapses and neural circuits, seeking treatment for mental illnesses such as anxiety, depression and schizophrenia by revealing approachable molecular targets and designing corresponding treatment strategies. The main research content is:
1) Research on the neural circuit of emotional and affective disorders
2) Pathogenesis study of neuropsychiatric diseases such as anxiety, depression and schizophrenia
3) Basic and clinical research on neuropsychiatric diseases such as anxiety, depression and schizophrenia (Clinical)